Grasshoppers play an important role in the ecosystem by contributing to nutrient cycling. Love them or hate them, they are bound to return year after year to repeat the same process.
Adult grasshoppers live for 30 to 60 days. The life cycle of grasshoppers is about 1 year, with all the stages of egg, nymph, and adult. Less than 20% of nymph grasshoppers survive to adulthood. Availability of food, climate, weather, predators, and pest control account for high mortality rates in grasshoppers.
Stay with us as we take a closer look at how these factors contribute to the low survival rates of grasshoppers in the wild. Also, if you are looking for an unconventional pet we will see if maybe grasshoppers could be an option for you.
Factors That Contribute To Grasshoppers Low Survival Rate
There are several factors that contribute to the low survival rate of the grasshopper species. We have broken these into four categories:
- The availability of food
- Seasonal changes and/or weather events
- The grasshoppers predators
- Human intervention and pest management
1. The Availability of food
Grasshoppers go through cycles, from the nymphs emerging from the eggs to molting five to six times before finally reaching adulthood.
As adults, they will spend approximately two weeks fattening up before mating and laying eggs, and then dying.
The availability of food will also influence the lifespan of grasshoppers. Both young nymphs and adult grasshoppers have extremely big appetites and can destroy large amounts of vegetation in a short amount of time.
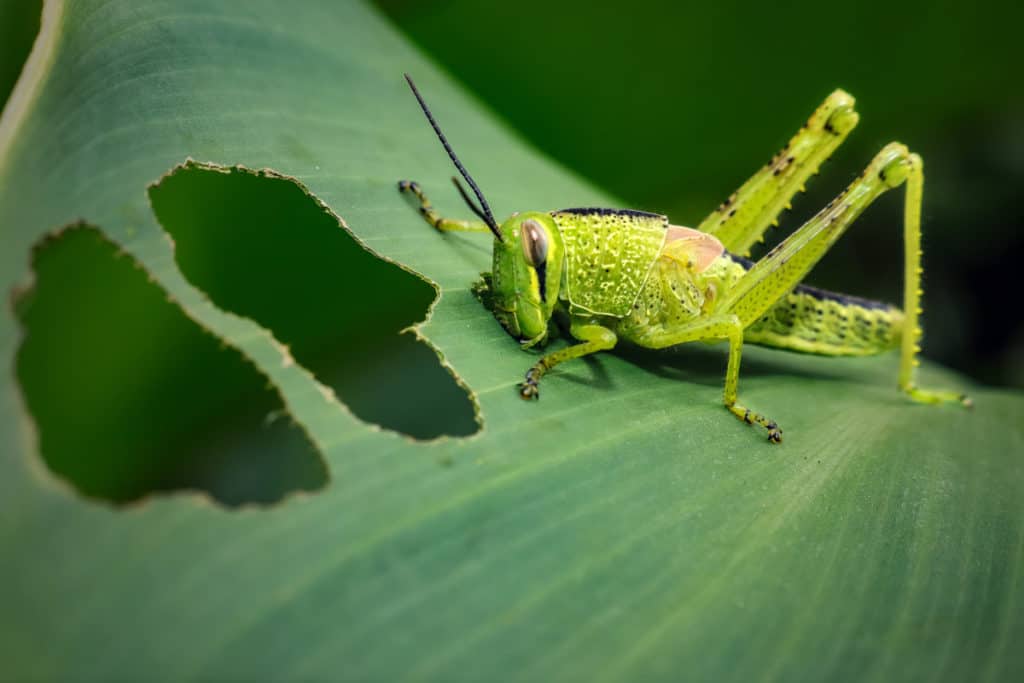

An average grasshopper can consume about half its body weight in food a day. They are known to eat away at anything from grass and leaves to cereal crops – pretty much any plant in sight.
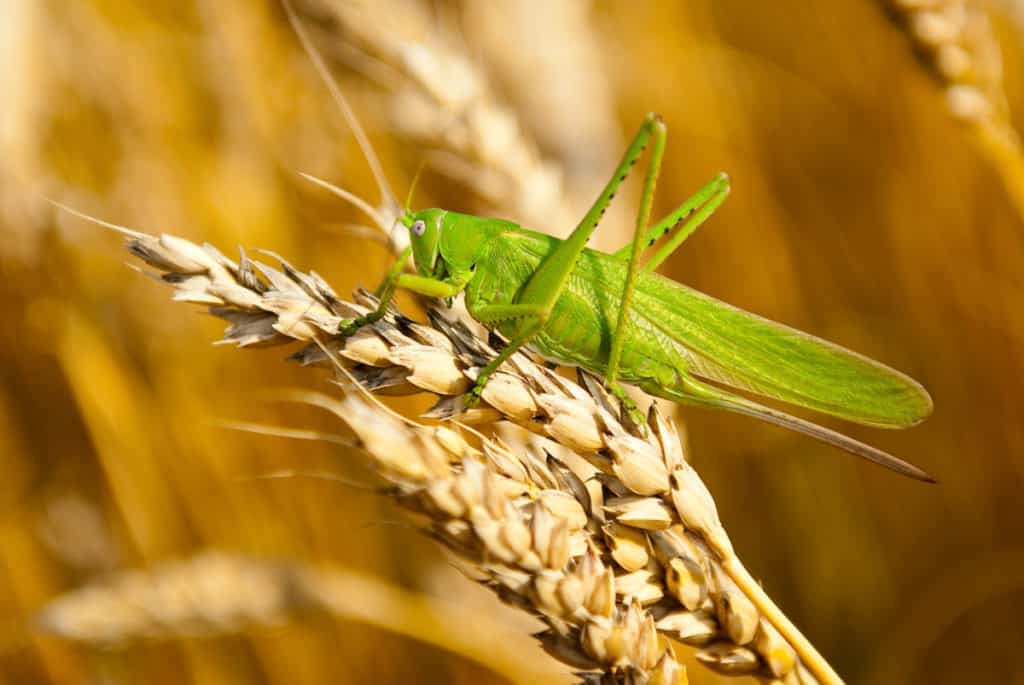

After emerging from the egg (nymph stage) the young grasshopper does not have wings or strong hind legs and is therefore at a higher risk of death. During this stage, they need to constantly feed in order to molt and develop into an adult grasshopper.
If there is not enough food available, the nymph will not have sufficient energy to make the transition.
It is clear grasshoppers have the ability to chew through acres of crops very quickly. This made us ask ourselves, could grasshoppers bite people? If you were caught up in a swarm of grasshoppers would they bite you?
We did the research. If you are interested in what we discovered check this article out, Do Grasshoppers Bite?
2. Seasonal Change And/Or Weather Events
Although some grasshopper eggs require cooler weather to hatch, grasshoppers thrive in hot, dry conditions.
Insects are cold-blooded, which means they rely on outside temperatures to regulate their internal heat.
In warmer weather, they eat more and in turn grow faster. Grasshopper eggs are also extremely vulnerable to fungal infection.
Cool damp weather makes eggs extremely susceptible to egg rot and parasitic attacks. Warm dry weather conditions help prevent the spread of the fungus, and therefore more eggs hatch successfully.
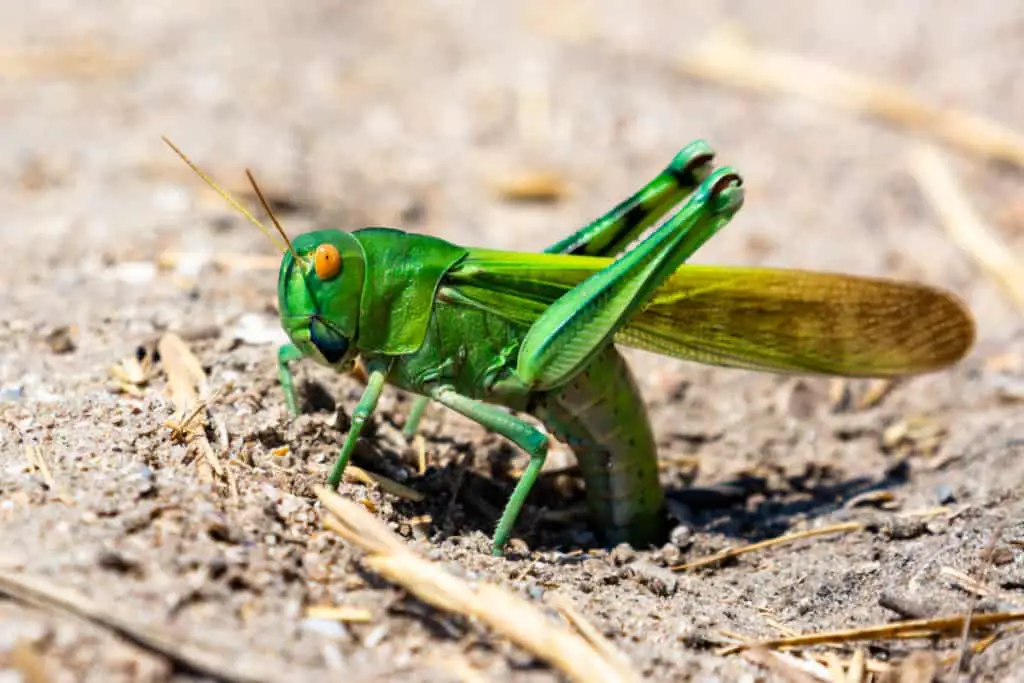

Warmer weather can also cause grasshoppers to swarm, and destroy huge amounts of vegetation in a short amount of time, thus showing how warmer weather is favored by adult grasshoppers as well as the young.
The eggs laying stage of the grasshopper’s life cycle is quite fascinating. If you are interested we have an article specifically about this called, Do Grasshoppers Lay Eggs?
3. The Grasshoppers Predators
Grasshoppers have numerous enemies in the wild, but one advantage is that they can easily jump away to escape danger, should they see, or hear it coming.
Grasshoppers are also able to leap many times their body length, thanks to their springy back legs. When jumping does not get them away from danger, adults can use their wings to assist them in the getaway process.
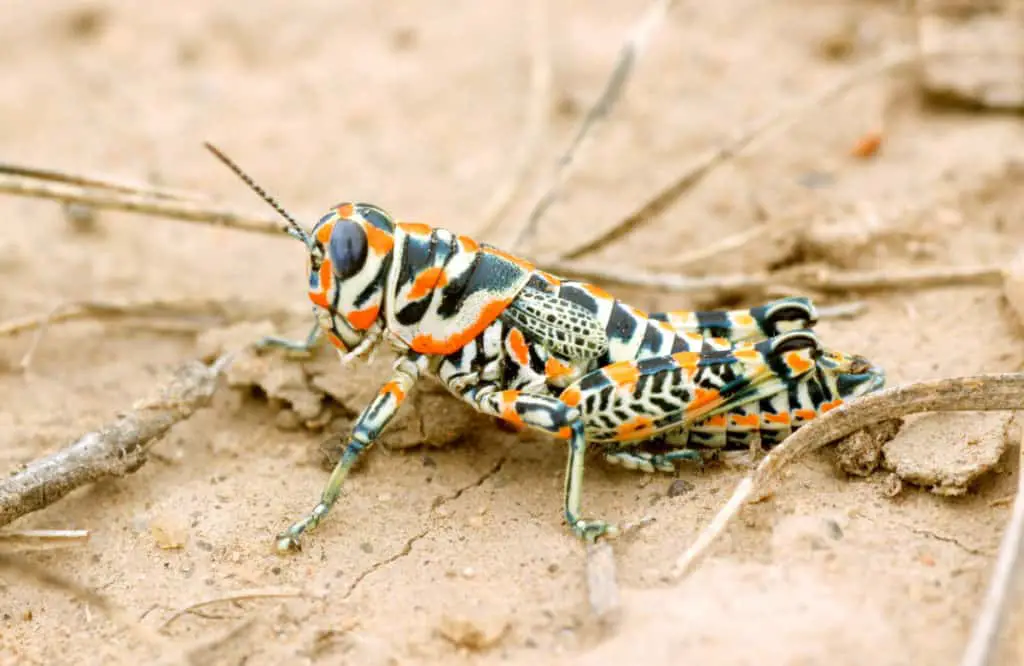

Another way to deter predators is color. Grasshoppers are often brightly colored as a warning sign to predators that they taste bad, or are poisonous. Some grasshopper species can spit a brown liquid onto predators if they feel threatened.
There are plenty of insectivorous birds that would make a quick meal of a grasshopper in the wild.
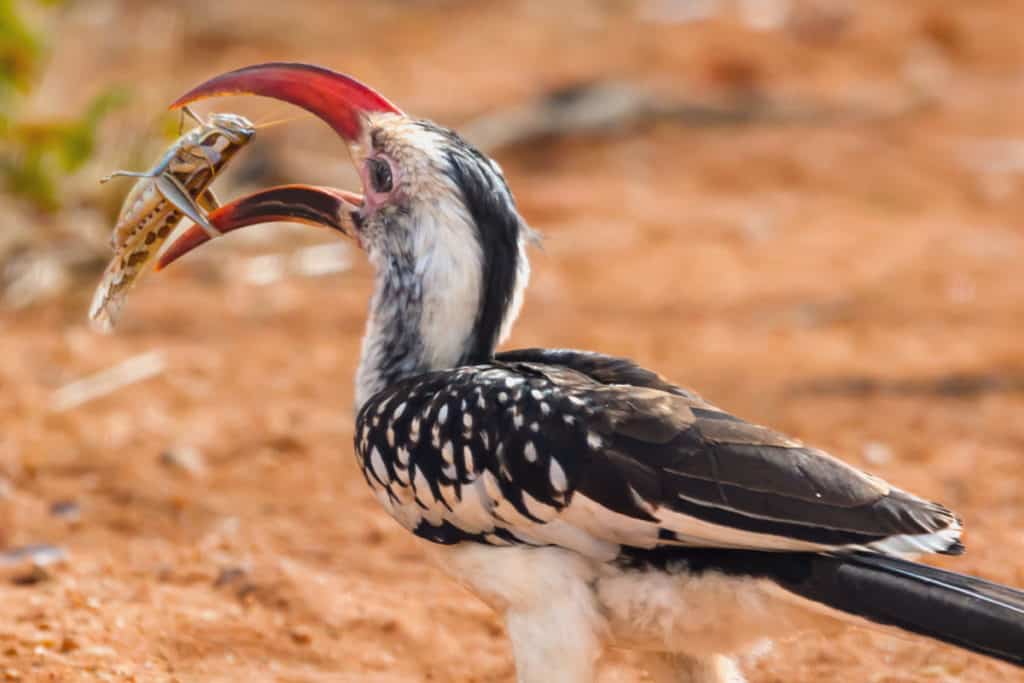

Domesticated birds such as chickens and geese also predate on them. Small mammals such as mice, raccoons, bats, and foxes will add grasshoppers to their list of delicacies.
Furthermore, frogs, some snake species, fish, and even turtles will grab this juicy snack. Above the threat from moving predators, the eggs of a grasshopper, as mentioned before, are threatened by a fungal infection.
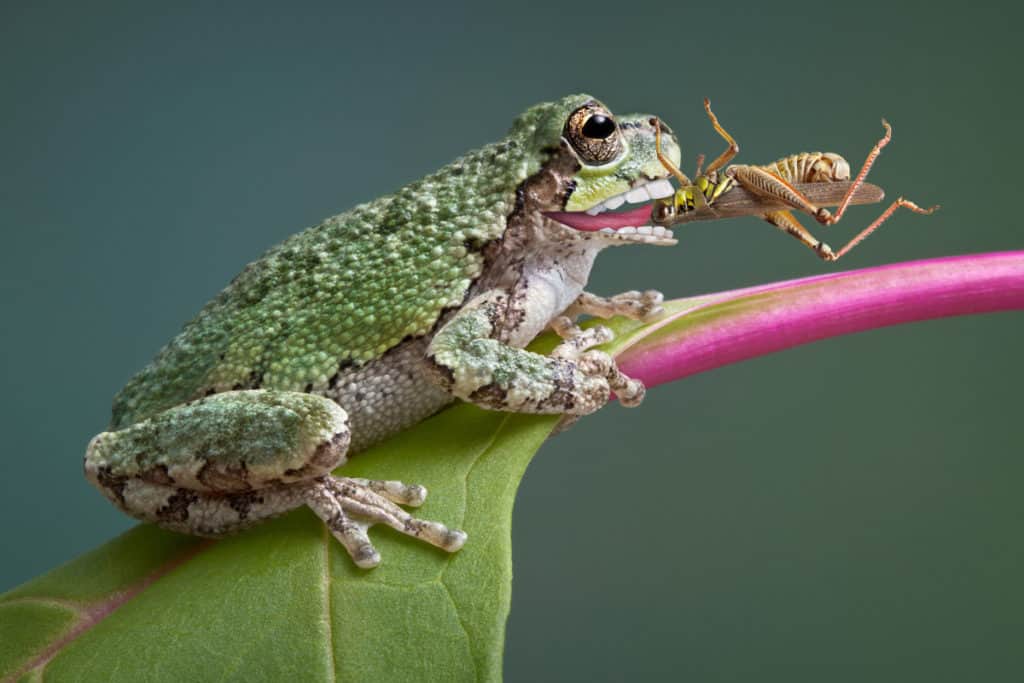

When in the nymph stage, grasshoppers are particularly vulnerable to predators. They do not have the ability to fly away and are continuously molting, which leaves them without a protective exoskeleton for a time.
Lastly, humans are one of the largest predators that grasshoppers face. Insects such as grasshoppers are rich in protein and many countries in Africa and Asia eat insects.
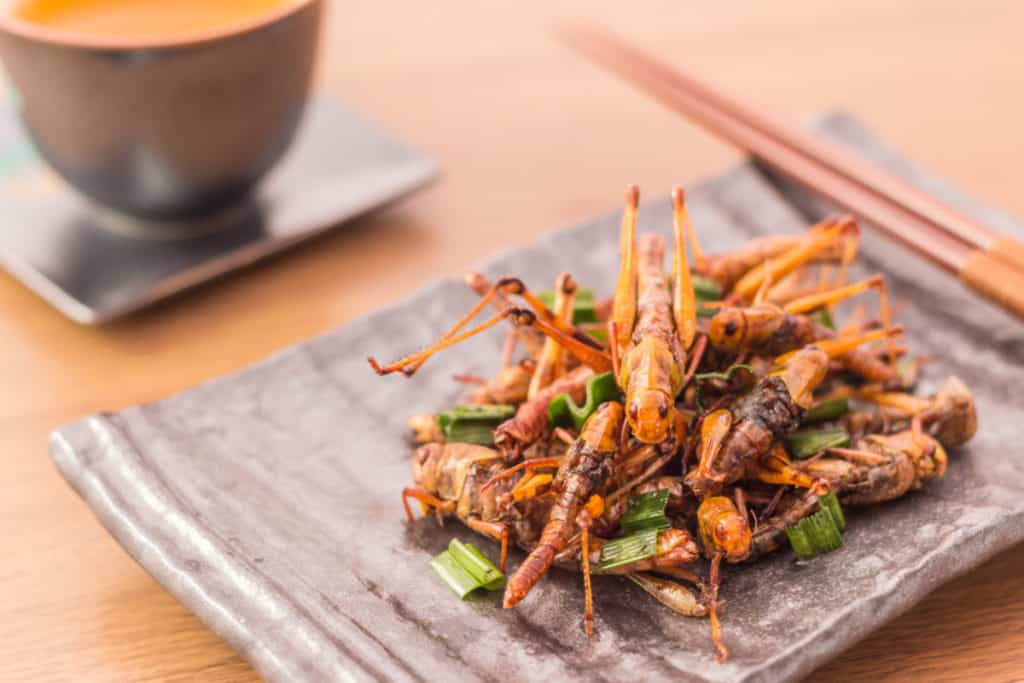

In Bangkok, grasshoppers are added to pad thai and in Uganda, they are served as a delicious treat. These insects contain large amounts of protein, but also contain loads of calcium, magnesium, and zinc. It is only in some countries in Europe and in the United States where eating insects is not done.
Another question we have been asked is about ants. Are ants friends or foes? Do grasshoppers eat ants or do ants eat grasshoppers? We take a good look at this in another article called, Do Grasshoppers Eat Ants? Or is it the other way around?
4. Human Intervention And Pest Management
Because of the grasshopper’s ability to congregate together and swarm – a process brought on by serotonin, they can be a pest and threaten food security. Grasshoppers can cause extreme damage to plants and vegetation.
While healthy ecosystems attract natural predators that can keep pests such as grasshoppers from greenery, this may not be a solution for crop farmers exposed to swarming masses.
It is believed that grasshoppers can be responsible for up to 25% of crop losses in some areas. They are not picky eaters and will decimate anything from grains to corn, rice, tobacco, and even a large variety of vegetables.
For this very reason, crop farmers take various measures to get rid of grasshoppers in their fields by using pesticide sprays. There are various methods to deter and control these critters. Tilling fields can prevent eggs from hatching.
It is not only the pesticides used by farmers and gardeners alike that threaten grasshoppers.
The constant expansion of cities and agriculture limits the natural breeding areas for grasshoppers. Loss of habitat is a major threat to almost all flora and fauna species in the world, and grasshoppers are not exempted from this danger.
Do you live in Flordia? Check out this article detailing the grasshoppers you will find in your state. Grasshoppers In Florida: Your Complete Guide
Can You Keep Grasshoppers As Pets?
Not everyone wants a dog or cat as a pet and grasshoppers can be an interesting companion, as long as you know what you let yourself in for. Grasshoppers, unlike dogs and cats, will not live for many years.
Caring for grasshoppers is relatively easy. You will need a large fish tank, filled with soil or substrate at the bottom of the tank.
Add twigs and foliage for your grasshopper and feed him daily with greens – it can be as simple as grass clippings. However, grasshoppers are extremely vulnerable to fungal infections, so you will have to remove all uneaten food daily to prevent it from growing mold.
You will have to decide whether you want more than just one grasshopper, but keep in mind that in many species, the adults die shortly after mating, and the female will die after laying her eggs.
The eggs will soon reveal nymphs. These look like adults, but just much smaller. In this case, you will get to witness the cycle and see the little nymphs molt and eventually make it to adulthood.
If you are still deciding if you want a grasshopper as a pet, you might also consider a praying mantis. We have written a detailed article comparing both these insects. Check it out if you are interested, Grasshopper Vs Praying Mantis.
How Long Do grasshoppers Live In Captivity
Although the full life cycle of a grasshopper can be up to one year, in the adult stage of its life, a grasshopper will only live for up to 7 weeks.
This time period is only true in ideal conditions, where the weather is good, and there is a lack of predators.
Keeping a grasshopper as a pet, or in captivity will also affect their survival rate.
The lifespan of a grasshopper again depends on the species, and the type of care provided.
Different species may have different lifespans and in the wild, but when kept in captivity you reduce the risk of predators, and are able to control the temperature and food quality.
Because these outside factors have been removed, it is possible for a grasshopper in captivity to live beyond a year. Although the females generally die after laying eggs, this is usually due to the weather and not their genetics.
The Wrap Up
Grasshoppers live for a year on average. This is inclusive of the egg, nymph, and adult stages.
An adult grasshopper can live up to 7 weeks in the wild, but it is less than 20% of nymphs that even make it to a fully grown adult.
Grasshoppers are extremely sensitive to temperature because they are cold-blooded. This, mixed with a limitation of food, and the large number of predators that feed on grasshoppers can greatly shorten their life expectancy.
If you have found this article interesting, we do have another article that explores the full lifecycle of grasshoppers called, The Lifecycle of Grasshoppers.
Sources
https://www.canolacouncil.org/canola-watch/2017/07/19/grasshoppers-thresholds-and-dry-conditions/
https://www.canolacouncil.org/canola-watch/2013/07/17/grasshopper-thresholds/
https://animals.mom.com/grasshoppers-enemies-7873.html
https://ecotourism-world.com/can-grasshoppers-be-a-sustainable-food-source-of-protein/
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/when-grasshoppers-go-bibl/
https://www.thespruce.com/control-grasshopper-garden-damage-2656303
https://www.planetnatural.com/pest-problem-solver/lawn-pests/grasshopper-control/