Spiders may not be everyone’s favorite, but they sure are fascinating creatures. Although most of them are harmless, people often opt to exterminate these pests in the home, with the most important part of spider extermination being the removal of spider eggs.
For the successful elimination of spider eggs, it is important to know how long it takes for spider eggs to hatch.
As a general rule, spider eggs hatch within 2 to 3 weeks, depending on the season and the spider species. Typically, egg sacks are either hidden in their web or carried by the female depending on the species. Once the spiderlings emerge from the egg, they’ll stay close to the nest for a few weeks.
Read on to find more about spider eggs, including their success rate, where spiders lay eggs, how many eggs spiders lay, how spiders protect their eggs, and finally, how to get rid of spider eggs.
The Life Cycle Of A Spider
The lifespan of spiders averages nearly two years, but it can vary with different species. Research suggests that female spiders live longer than males, as the male spiders die soon after mating.
The life cycle of a spider can be divided into three phases:
- Egg phase
- Spiderling phase
- Adult phase.
Egg Phase
Mating in spiders involves inserting sperm into the epigynum, the female genital structure seen under the abdomen. Following mating, the female spiders store the sperms until it is time to produce eggs.
Prior to laying eggs, females set up a silk egg sac to protect the developing offspring. The silken egg sacs are usually hidden in the web or carried by the mother spider. Mother wolf spiders are known to carry their eggs with them wherever they go.
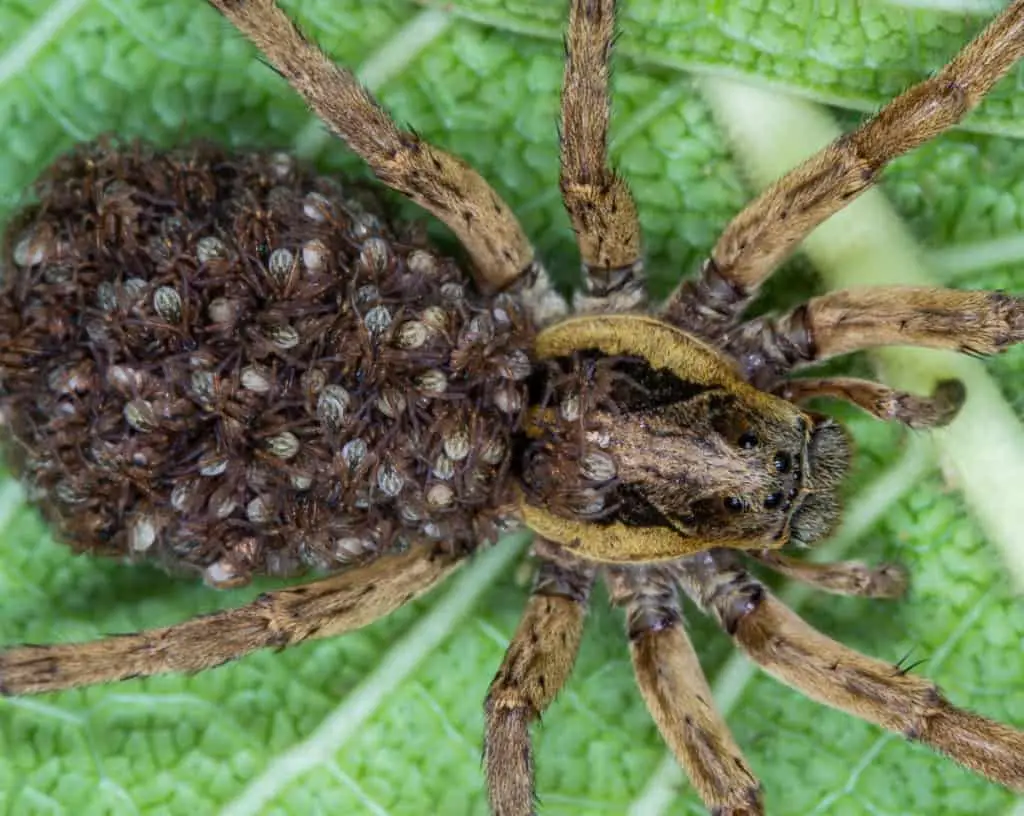

Once the sac is ready, the female spider deposits eggs inside it. A single egg sac may contain up to several hundred eggs. The number of egg sacs constructed by female spiders differs based on the species.
The mother spiders protect the egg sacs from predators and other challenging environmental conditions until they hatch. Spider eggs generally hatch in two to three weeks, but it depends on the species and season.
Spiderling Phase
Also known as the immature phase, the spiderling phase involves all the tiny spiders moving out of the egg sac and scattering around.
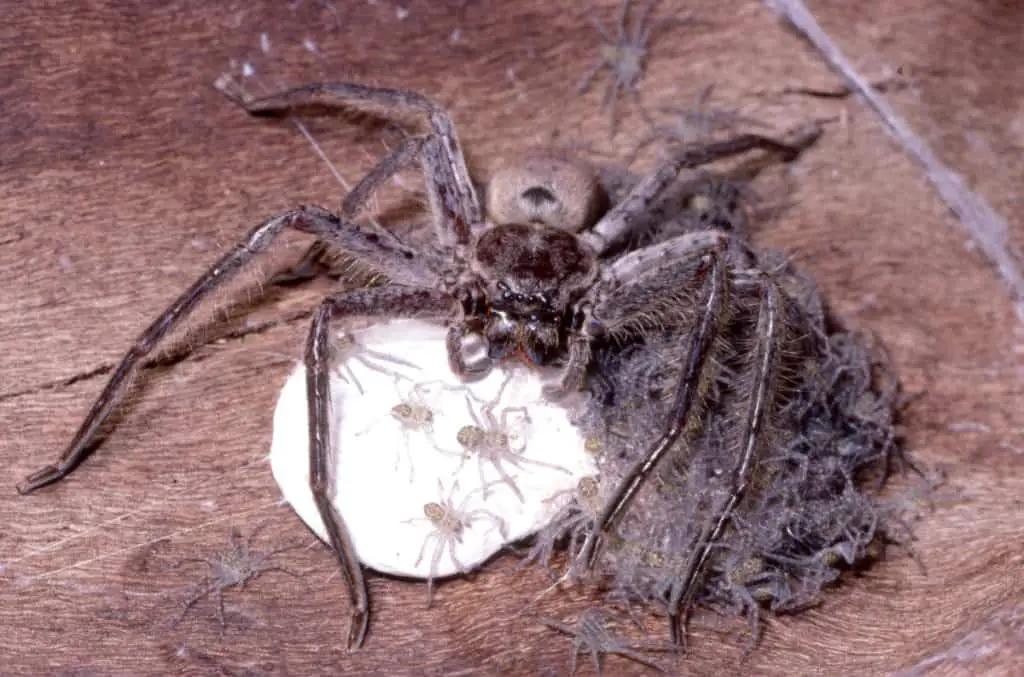

Most spiderlings exhibit a behavior called ballooning or kiting, where they release threads of silk into the air by raising their abdomens. The wind catches these threads and carries the spiderlings away.
The juniors then undergo a process called molting, during which the inner layer is broken down to release the nutrients. The spiders reabsorb these nutrients for later use. Frequent molting results in the formation of a large exoskeleton following the shedding of the old one.
Some spiders continue to molt throughout their life. Research also suggests that females take more time to mature when compared to males, as female spiders are larger than male spiders.
Adult Phase
The adult phase or the sexually mature phase is when the spiders are ready to mate to keep the life cycle going. Males usually die soon after mating, apparently due to the expansion of the appendages on the spider’s head called pedipalp.
Spider cannibalism is an interesting phenomenon seen during the adult phase in some species. It involves the female spider eating the male spider during or after copulation. Research links this behavior with the aggression of female spiders.

Where Do Spiders Lay Their Eggs?
Female spiders spin silk egg sacs in which they lay their eggs. This is followed by spinning even more silk to cover the egg sac to provide extra protection. These sacs, which look like white round balls, are usually hidden in spider webs, affixed to a surface, or carried by the female spider (attached to her abdomen).
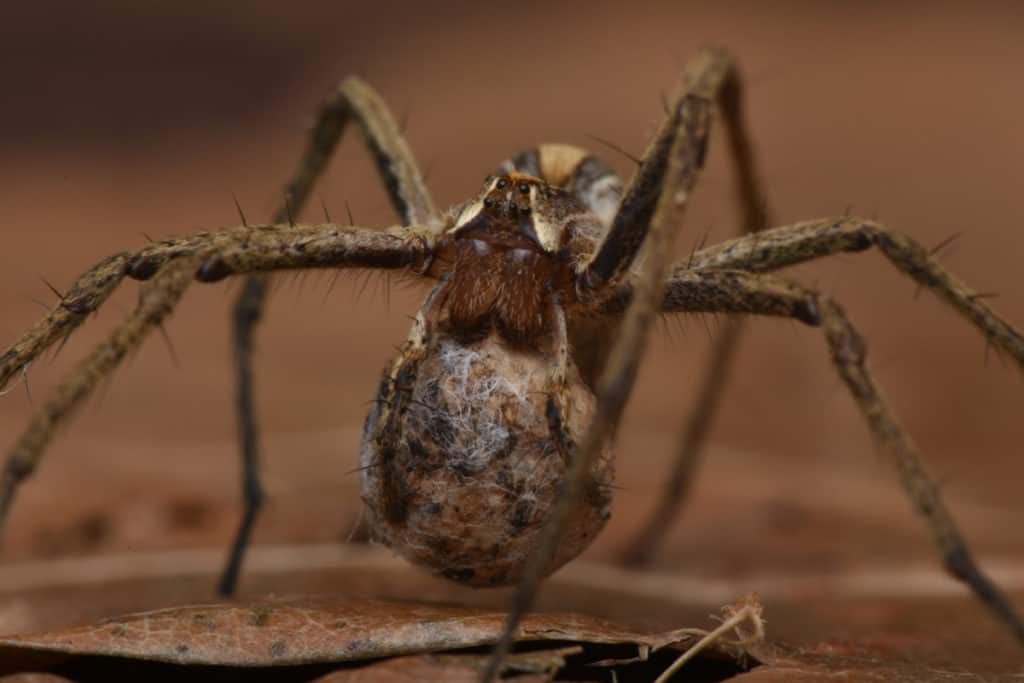

Spiders are most likely to dwell in dark and humid corners of the house. You may be able to find spider egg sacs affixed to surfaces in these areas.
If you are interested we have two articles that discuss these dark corners and why or why not some species are attracted to the light or the darkness. These articles are:
Are Spiders Attracted to Light?
What Time Of Year Do Spiders Lay Eggs?
Typically, spiders lay eggs all year round, but it varies with the species. For instance, hobo spiders lay eggs in September and October, whereas wolf spiders lay eggs during the summer season.
The male spiders protect the females until the winter season. Some males die after mating, while others do not. Spider eggs usually remain the same during winter and hatch during spring or late summer.
A common question we get asked is if spiders hibernate over the winter. We have some answers to this question in another article we have written called, Do Spiders Sleep?
How Many Eggs Do Spiders Lay?
Spiders can produce several egg sacs, where each sac may contain several hundreds of eggs.
The number of eggs spiders lay ranges from 2 to 1000, depending on the species. For instance, female black widow spiders can produce 10 to 20 egg sacs, each sac containing 150 to 300 eggs.
Do Spiders Protect Their Eggs?
Yes, spiders protect their eggs by wrapping them in a silk egg sac until the spiderlings come out.
Once the eggs are safe inside the sacs, the mother spider may attach the sac to a surface or carry it on her back. Mother spiders of some species even drag the sacs with them wherever they go.
How Do You Get Rid Of Spider Eggs?
Spider eggs can be removed using a vacuum cleaner or broom. While vacuuming, ensure that no spiderlings escape the dustpan. Once all the eggs are collected, move them into a sealed plastic bag and clean the vacuum cleaner thoroughly.
Spider eggs are brittle, so most of them will die immediately after being sucked into a vacuum cleaner.
How To Prevent Spider Infestation Naturally
Spider infestations are undoubtedly scary. Therefore it is always better to discourage spiders from finding comfort in your home.
Here are a few actionable steps you can take to prevent spider infestation:
Control Food Sources
The best way to prevent a spider infestation is to control their food sources around your house because, just like any other pest, spiders also love hanging around food.
As spiders primarily feed on insects, make sure that there are no other insects in or around your house. These include mosquitoes, cockroaches, moths, fruit flies, and more.
For a complete guide on want spider eat check out this article we have written, What Do Spiders Eat?
Reduce Clutter
Less clutter means less space for spiders to hide. Remove the empty boxes, unwashed clothes, and piles of newspaper lying around. Ensure that your yard is also clean. Keep firewood away from the house and remove other organic debris.
Another important tip is to vacuum frequently. Pay special attention to corners, basements, and dark and humid rooms.
Seal Cracks
Always close cracks and gaps in your homes to prevent spiders and other pests from entering inside. Apply tape or use sandpaper to level the cracked area with the rest of the wall.
Keep in mind that the doors and windows should fit tightly in their frames, leaving no space in between.
Use Glue Traps
You can also use glue traps to get rid of spiders in your house. Place the traps behind the furniture, attics, storage spaces, and dark and humid areas. Use non-toxic glue traps, especially if you have pets at home.
The Wrap Up
To conclude, spider eggs hatch within 2 to 3 weeks, depending on the season and the species. Once the eggs hatch, the spiderlings will scatter around and find their own territory.
Most spiders are not harmful to humans. In fact, they prevent other pest infestations. However, spider infestations can be scary, so it is better to take necessary precautions to prevent these arthropods from entering your home.
Controlling spiders is pretty easy as they are loners and not social insects. Use glue traps, declutter, clean dark and humid areas, and seal up all the cracks and crevices in your home. But be careful when you deal with spider eggs, as hundreds of spiderlings can come out of a single egg.
If you are interested in other bugs and their eggs then check out these ather article we have written:
Do Praying Mantis Die After Laying Eggs?
Sources
https://journeynorth.org/tm/spring/SpiderLife.html
https://www.prevention.com/life/a33533075/spider-eggs/
https://www.quora.com/Where-do-spiders-lay-eggs
https://www.thoughtco.com/the-spider-life-cycle-1968557
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epigyne