While the irrational fear of spiders is one of the most common phobias, most of these creatures with bad rep are harmless. Arachnophobia can however be justified considering that female spiders lay anything from 200 eggs to 1000 eggs in an egg sac.
However, depending on the number of times they are fertilized, they could produce up to nine of these egg sac parcels at any given time.
These are either carried with the female or in the web in the case of web-building species.
But, what are these baby spiders called once they have hatched?
These freshly hatched spiders are known as spiderlings. They are called spiderlings until they reach adulthood, which could be between five and ten molts depending on the species. Some are cared for by their mothers while others are left to fend for themselves.
Read on to find out more about the lives of baby spiders.
Are Baby Spiders Cared For By Their Mother?
Female spiders create a silk surface to lay eggs and then cover the eggs in a silk cocoon for safety. It is from this cocoon where the spiderlings will emerge, and the female spider will guard it until the little spiders emerge.
While many spiderlings will have to fend for themselves as they disperse from the web, there are some exceptions.
Wolf Spiders
Some spiderlings start off their life a little easier than others, as is the case with wolf spiders.
Female wolf spiders are good mothers. They will carry the egg sac with them until they hatch, and then the spiderlings will climb on her back until they are fully developed, which could take weeks.
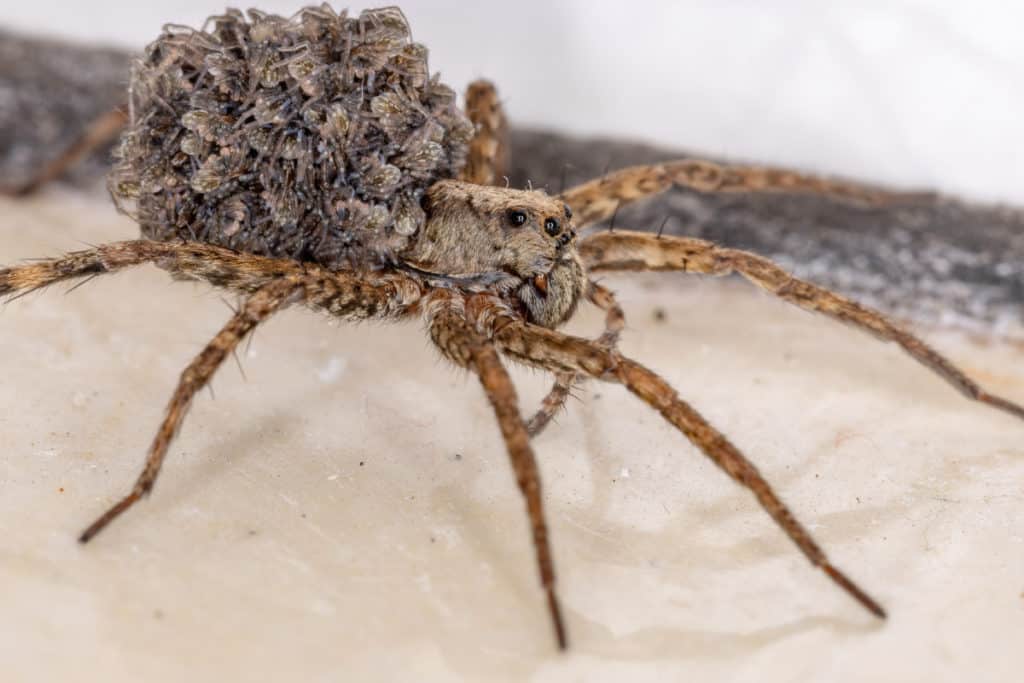

Wolf spiderlings even go hunting with the mother, and if a spiderling falls from the mother, she will wait for it to climb back on.
During the time on the mother’s back, the spiderlings live off the egg yolk from the eggs from which they emerged.
Crab Spiders And Velvet Spiders
These two species, amongst others, show some unusual and rather grotesque behavior called matriphagy, or the act of spiderlings eating the mother.
The mother will first spend time feeding the babies with a liquefied version of food, and then later, the mother will be eaten by the spiderlings.
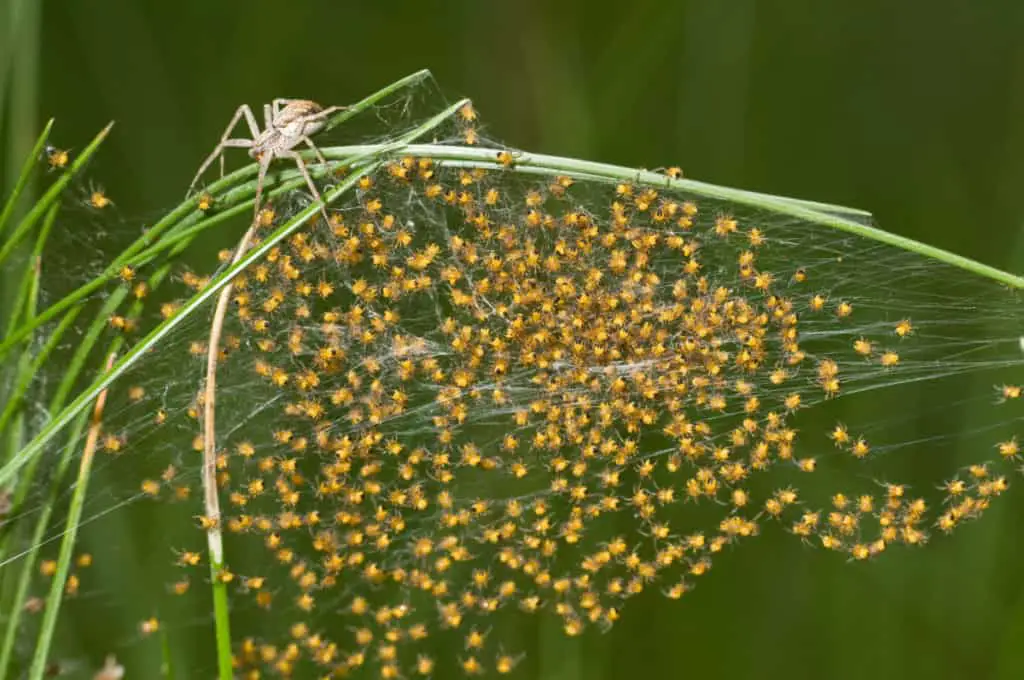

While this is uncommon in the animal kingdom, it is not completely strange in the spider world.
Certain Jumping Spiders
Research shows that mothers of some jumping spider species feed their spiderlings with a type of “spider milk” and continue to do so, long after they can fend for themselves.
These mothers tend to their young, maintaining the nest, and removing parasites, effectively giving the spiderlings a greater chance of survival.
How Big Are Spiderling When They First Hatch?
The size of spiderlings upon hatching depends on the type of spider, as not all spiders are the same size. Some spiders remain small even as adults while others can reach the size of a dinner plate.
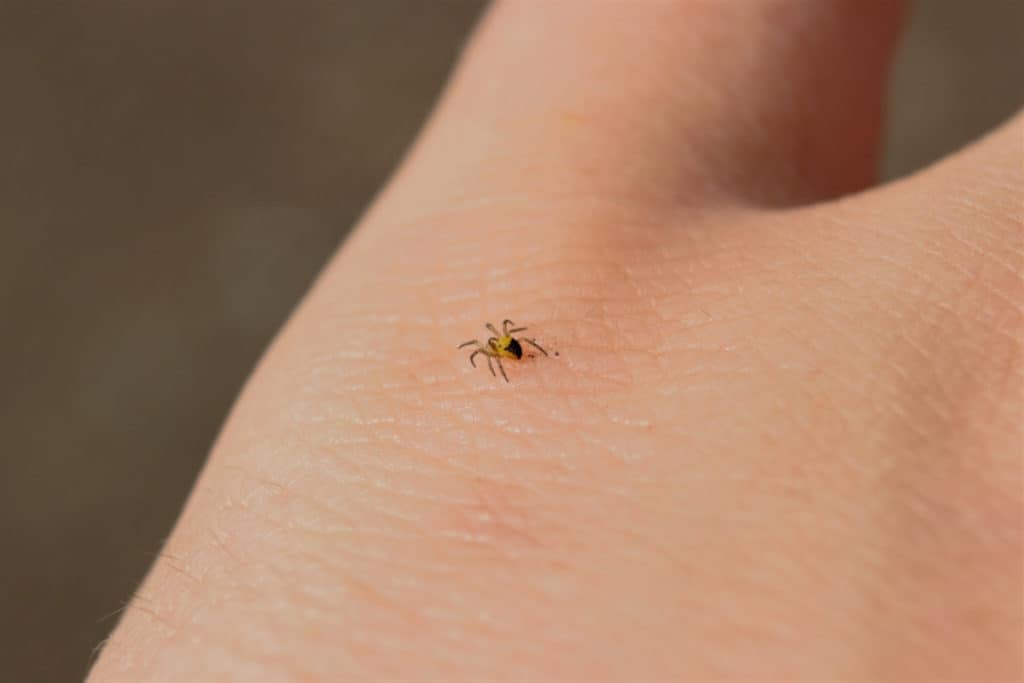

Spiderlings look exactly like adult spiders but are much smaller. When they hatch, they do not have fully-developed reproductive organs.
Where Are You Likely To Find Spiderlings?
Spiderlings are likely to stay inside the egg sac for the first stages of their lives while they are in the developing stages. They emerge as baby spiders-at this stage they eat the egg and eventually molt.
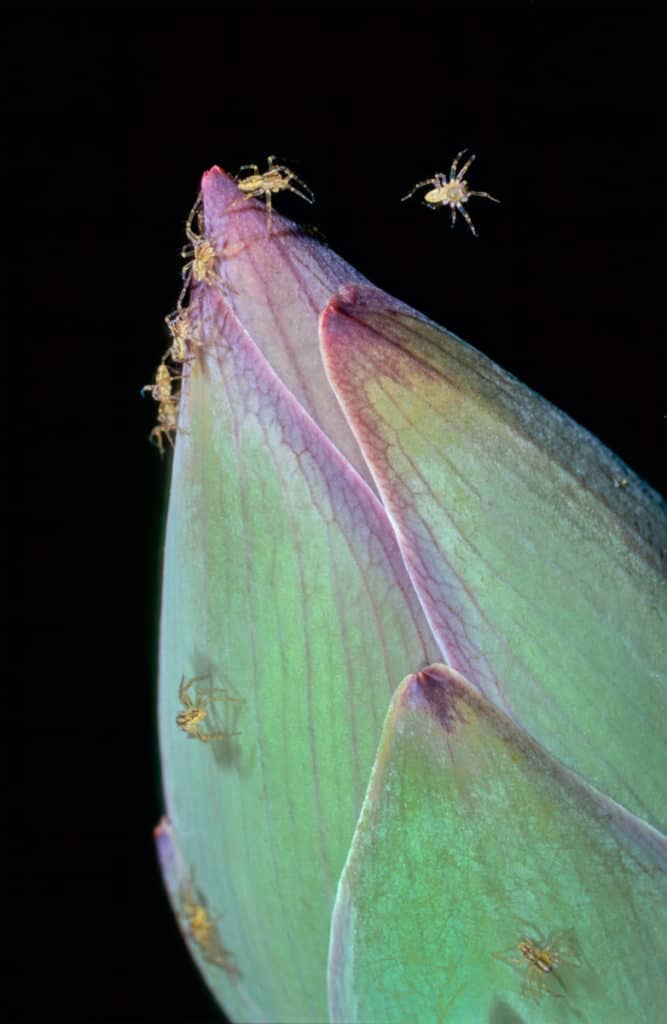
Depending on the species, they start dispersing after the second molt. The way they disperse again depends on the species.
Some spiderling species disperse by bridging and ballooning, where they will float long distances through the air by anchoring a piece of silk strand and using the air to travel to a new location. Ground and burrow-dwelling spiders disperse by walking.

When Does A Spiderling Become A Spider?
Spiderlings reach adulthood once they have molted five to ten times on average. This of course varies between different species. It is also believed that male spiders mature earlier and have fewer molts, two to eight, while females will molt anything from six to twelve times before reaching maturity.
What Time Of Year Are You Likely To See Spiderlings?
While there’s no exact time frame, most female spiders mate, and lay eggs in the fall. The young spiderlings overwinter in the egg and emerge in spring when the weather gets warmer, but some spiderlings might even hatch in autumn or during winter.
When it comes to the common house spider, brown house spider, domestic house spider, mating can take place year-round. The giant house spider, known as the Greater European House Spider is another species that seeks mates during the late summer and fall months.
What Is The Survival Rate For Spiderlings?
It is a harsh world out there and most spiderlings are tiny and extremely vulnerable due to their soft, fragile bodies.
In species where the adults look after the youngsters, their survival rate will be a lot higher.
The ant-mimicking jumping spider mother feeds the spiderlings a protein-rich milk fluid that contains nearly four times the protein of cow’s milk, helping them grow quickly.
The study published in Science shows that the spiderlings had a much better chance of survival to adulthood as they finally left the nest much stronger.
There are many predators once they leave, and this includes lizards, fish, birds, wasps, centipedes, primates, scorpions, and even other spiders.
What Do Spiderlings Eat?
In the early stages of the spiderling’s life, they will feast on the egg they emerged from. Some species take the liquid fed by their mothers. In species that practice matriphagy, the mother spider will be their first meal before dispersing.
In some cases, spiderlings even resort to cannibalism i.e they eat their brothers and sisters. They eat their brothers and sisters. There is a lot of cannibalism going around, and spiderlings often eat one of their siblings when they first emerge from the egg sac.
It’s not a pretty thing to think about, but that is just how it works.
Some species, however, like the black widow may stop their offspring from feasting on their own, by putting them on an even playing field.
Without maternal intervention, “the offspring might turn on each other and start eating others because that’s what spiders do,” Chadwick Johnson, a biology professor at Arizona State University and the lead author of a recent study on black widows published in Animal Behavior told the Washington Post.
Larger spiderlings mixed with smaller brothers and sisters would most likely predate on the inferior siblings in a matter of a few days.
Surprisingly, spiderlings also eat pollen as these small particles landing on the web can contain up to 61% protein. When they are a little bigger, they can eat tiny fruit flies.
Across different species of spiders, the diets can be wide a varied. If you want more information check out this article we have written, What Do Spiders Eat?
The Wrap Up
Adult spiders can have hundreds of babies at a time. Each of these baby spiders represents a smaller version of their adult selves.
Although baby spiders, also known as spiderlings, are miniature replicas of their adult selves, they will need to go through multiple moltings in order to grow into their full selves, as well as to develop the required organs for reproduction.
Each species will differ, as it is with most of the animal kingdom. Keep an eye out for baby spiders in your house. It could be an amazing experience to watch them grow and see how they move from their nest into their new homes.
Sources
https://sciencing.com/many-can-house-spider-lay-7753581.html
https://www.britannica.com/animal/spider-arachnid/Eggs-and-egg-sacs
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/news/2015/04/150421-wolf-spider-squashed-video-animals/
https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn27143-zoologger-the-baby-spiders-that-munch-up-their-mum/
https://www.aaas.org/news/jumping-spiders-nurse-offspring-nearly-adulthood
https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2018-07/cp-wsb062818.php
https://www.britannica.com/animal/spider-arachnid/Eggs-and-egg-sacs
https://journeynorth.org/tm/spring/SpiderLife.html
https://sciencing.com/common-house-spiders-mating-habits-6802490.html